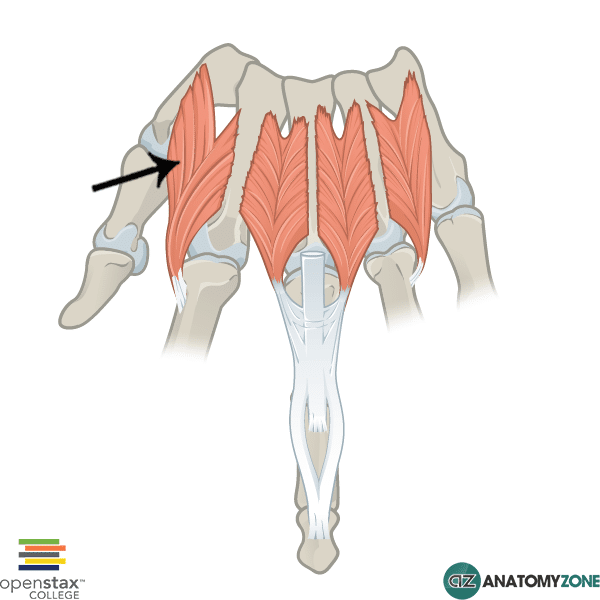
Dorsal Interossei
The structure indicated is the first dorsal interosseous muscle of the hand.
The dorsal interossei belong to the intrinsic group of muscles which act on the hand. The intrinsic muscles include the following muscles/groups:
- Thenar group (act on thumb)
- Hypothenar group (act on little finger)
- Adductor pollicis
- Lumbricals
- Interossesus muscles (dorsal and palmar)
- Palmaris brevis
All the intrinsic muscles of the hand, except the thenar muscles and the lateral two lumbrical muscles are innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. The thenar muscles and the lateral two lumbrical muscles are innervated by the median nerve. A useful mnemonic for remembering this is MEATLOAF. “MEAT” refers to the Median nerve, and LOAF refers to the muscles which it innervates: Lateral two lumbricals, Opponens pollicis, Abductor pollicis brevis, Flexor pollicis brevis.
The interosseous muscles, as the name suggests are located between (inter-) the metacarpal bones (-osseus). There are 4 bipennate dorsal interossei located between the adjacent shafts of the metacarpal bones and insert onto the bases of the proximal phalanges and the extensor hoods. The dorsal interossei serve to abduct the fingers away from the central axis of the middle finger. The first interosseous muscle inserts onto the base laterally on the index finger.
The palmar interossei in contrast are unipennate in structure and function to adduct the fingers towards the central axis of the middle finger. A useful mnemonic for remembering this function is PAD and DAB: Palmar interossei AD-duct, Dorsal interossei AB-duct.
Learn more about the anatomy of the hand muscles in this tutorial.