External Abdominal Oblique Muscle
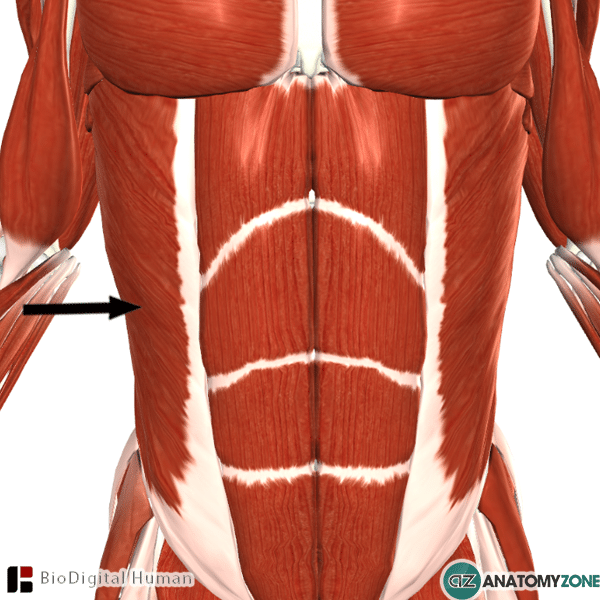
The muscle indicated is the external oblique muscle of the abdomen.
The external oblique muscle is the most superficial lateral muscle of the anterior abdominal wall. The three muscles which make up the lateral part of the anterior wall of the abdomen from superficial to deep are the:
- External oblique
- Internal oblique
- Transversus abdominis
Origin: ribs 5-12
Insertion: Iliac crest, pubic tubercle, linea alba
Innervation: thoracoabdominal nerve and subcostal nerve
Action: Flexion and rotation of the vertebral column – brings about contralateral rotation of the torso. Unilateral contraction causes lateral flexion of the vertebral column. Important in increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
The aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle is important, as it forms the inguinal ligament, which runs from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. The ligament forms the base of the inguinal canal.
The fibres of the external abdominal oblique muscle are oriented inferiorly and anteriorly – the fibres of the internal oblique are oriented perpendicular, running superomedially.
Learn more about the anatomy of the external oblique muscle in this tutorial on the anterior abdominal wall.




















