Anulus Fibrosus
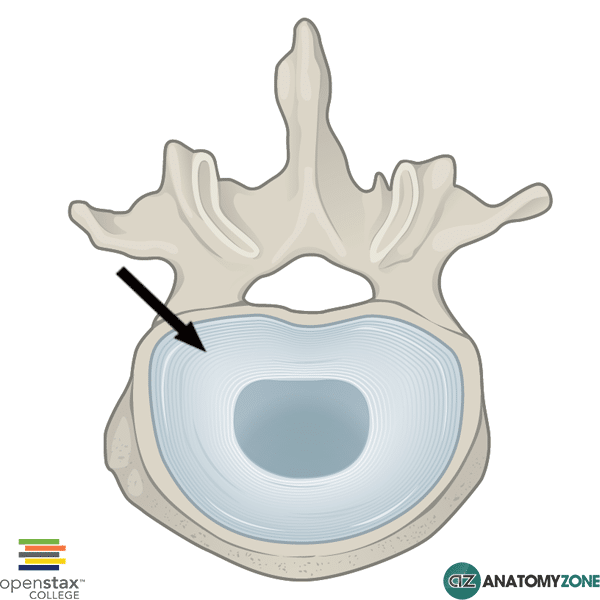
The structure indicated is the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc.
Intervertebral discs are found between adjacent vertebral bodies in the spinal column. Intervertebral discs are one of two major joint types found in the vertebrae, the other type being synovial joints between the articular processes.
The symphyses between the vertebral bodies consists of hyaline cartilage which lines the vertebral body, and an intervertebral disc which is sandwiched between the two adjacent intervertebral bodies to form this fibrocartilaginous joint.
The intervertebral disc consist of
- Anulus fibrosus (outer component)
- Nucleus pulposus (inner component)
The anulus fibrosus forms the outer fibrous portion, which envelops the inner gel-like nucleus pulposus. The anulus fibrosus consists of laminae of fibrous tissue and fibrocartilage – the organisation of this tough tissue into lamellae allow the intervertebral discs to sustain heavy compressive loads.
Disc prolapse occurs when the inner gel-like nucleus pulposus is forced out of the anulus fibrosis, thereby exerting pressure on local nerves, or the spinal cord.
Learn more about the anatomy of the vertebrae in this tutorial!