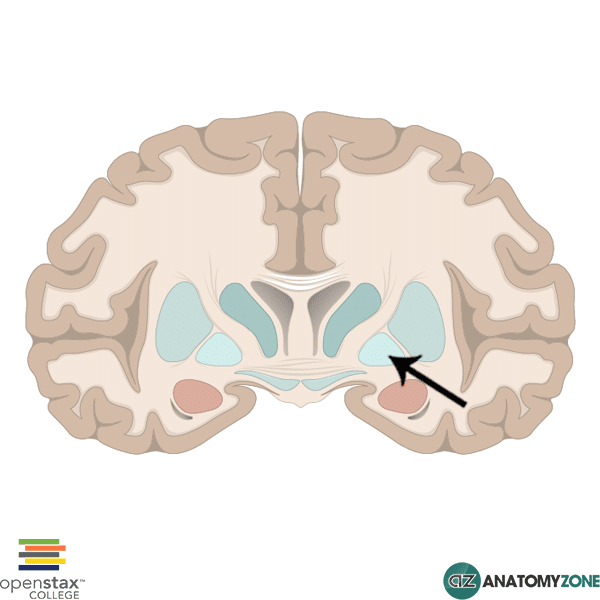
Globus Pallidus
The structure indicated is the globus pallidus.
The globus pallidus is a subcortical structure located within the cerebral hemispheres, and is a major component of the basal ganglia.
The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei (collection of neuronal cell bodies located within the CNS) located at the base of the forebrain. The term “basal ganglia” is a misnomer, and the name “basal nuclei” would be more appropriate, since ganglia are collections of neuronal cell bodies located within the peripheral nervous system. The basal ganglia form extensive connections with other areas of the brain and are involved mainly in the control of movement and posture.
The basal ganglia consist of the following main components:
- Caudate nucleus
- Putamen
- Globus pallidus
- Substantia nigra
- Nucleus accumbens
- Subthalamic nucleus
These components are grouped together as follows:
- Caudate nucleus + putamen = striatum
- Putamen + globus pallidus = lentiform nucleus
The globus pallidus lies medial to the putamen and consists of an internal (medial) and external (lateral) component, separated by the medial medullary lamina. The internal capsule runs medial to the lentiform nucleus. The posterior limb of the internal capsule separates the thalamus from the lentiform nucleus. The anterior limb of the internal capsule separates the putamen from the head of the caudate nucleus.
The globus pallidus is sometimes referred to as the pallidum, or the paleostriatum. The neostriatum is a term used to describe the caudate nucleus and putamen (striatum).
Learn more about the basic anatomy of the brain in this tutorial.