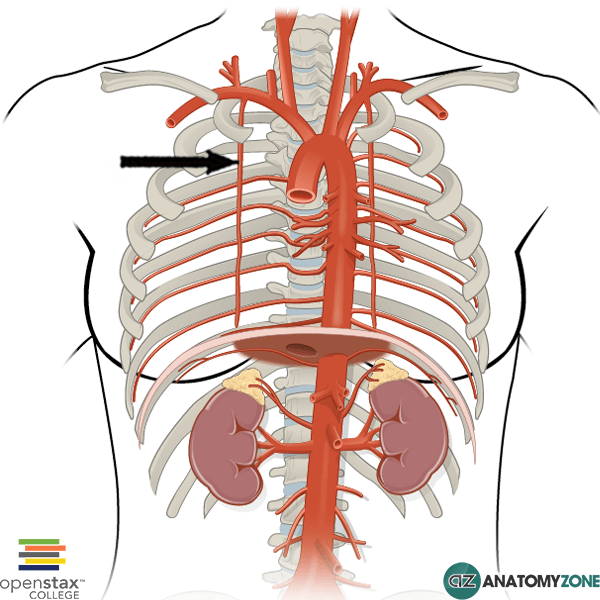
Internal Thoracic Artery
The structure indicated is the internal thoracic artery.
The internal thoracic artery was formerly known as the internal mammary artery and is an artery located anteriorly in the thorax. It is a branch of the subclavian artery.
The left subclavian artery comes directly off the arch of the aorta, whereas on the right side of the body, the brachiocephalic artery splits, giving rise to the right subclavian artery, and the right common carotid artery.
The subclavian artery becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. It can be thought of in three parts, and gives rise to several branches:
- First part: vertebral artery, internal thoracic artery, thyrocervical trunk
- Second part: costocervical trunk
- Third part: dorsal scapular artery
The internal thoracic arteries descend lateral to the sternum on either side, and give off several branches on the way, including the 12 anterior intercostal branches which anastomose with their counterpart posterior intercostal arteries.
The internal thoracic artery terminates by dividing into two branches: the musculophrenic artery and the superior epigastric artery.