Fibularis Longus
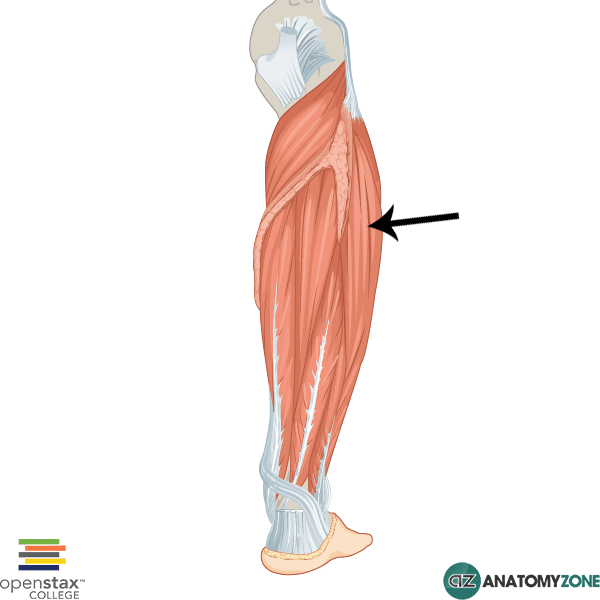

The structure indicated is the fibularis (peroneus) longus muscle of the leg.
The fibularis longus muscle is one of the muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg. The leg consists of three muscular compartments: anterior, posterior and lateral. The lateral compartment consists of two muscles:
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus
- Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
The lateral muscles are responsible for eversion of the foot and are innervated by the superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve, which is a branch of the common fibular nerve. The common fibular nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve and divides into the superficial fibular nerve and the deep fibular nerve. The deep fibular nerve innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg.
The tendon of the peroneus longus passes underneath the foot to insert medially on the base of the first metatarsal and the distal medial cuneiform bone. In doing so, it runs along a groove in the cuboid bone and forms a sling for the foot, supporting the transverse arch.
Origin: superior lateral surface of fibula
Insertion: plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone and base of first metatarsal
Innervation: superficial fibular nerve
Action: eversion and plantarflexion of foot.
Learn more about the muscles of the leg in this tutorial.